Have you ever wondered how doctors figure out what's really going on inside your body, especially when it comes to tiny invaders or specific body signals? It's a pretty big question, and there are many tools that help. One particularly clever method, a true "genius" in its field, is something we call ELISA. This test is a cornerstone in modern medicine and science, providing clear answers where guesswork just won't do. It's truly fascinating, you know, how much this one technique can tell us.
So, what exactly is this amazing method, this "elisa del genio," that helps us understand so much about health and disease? Well, it stands for Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay. It's a laboratory testing technique that's been around for a while, and it's used to find and measure very specific things in samples from living beings. This includes finding certain antibodies, antigens, proteins, and even hormones in different bodily fluids. It's a very precise way to get information, and it's used widely, you know, in so many places.
This method has a wide reach, truly. You'll find it used as a diagnostic tool in human medicine, helping to spot illnesses early. It's also vital in understanding plant health, helping farmers protect crops, and it plays a big part in biotechnology. Beyond that, it's a very reliable quality control check in various industries, making sure products are safe and effective. It's pretty versatile, you see, how it helps in so many different areas.
- Is Hannah Ricketts Married
- Two Babies One Fox
- Aayushi Jaiswal New Hot Web Series
- Hannah Owo
- Xxxx Is Equal To
Table of Contents
- Elisa: A Brief History and Its Development
- Key Characteristics of the Elisa Method
- How Elisa Works: The Core Principles
- The Many Uses of Elisa: Where It Shines
- Different Types of Elisa Assays
- Frequently Asked Questions About Elisa
- Looking Ahead: The Future of Elisa
Elisa: A Brief History and Its Development
To truly appreciate the "genius" of ELISA, it helps to know a little about its beginnings. The concept of using enzymes to detect immunological reactions first came about in the early 1970s. Scientists were looking for ways to find tiny amounts of substances in samples without using radioactive materials, which could be tricky to handle and dispose of. So, they wanted something safer and easier, too.
This new idea, using enzymes linked to antibodies, really changed things. It offered a very sensitive way to spot specific proteins or antibodies, and it quickly became a go-to method in labs all over the world. It was a big step forward, and it's still very much in use today, which is quite something, you know.
Key Milestones in Elisa's Journey
- Early 1970s: The first ELISA methods were developed, offering a safer alternative to radioactive immunoassays.
- Mid-1970s: Rapid adoption in research and diagnostic labs due to its sensitivity and ease of use.
- Ongoing: Continuous improvements in reagents, automation, and assay design make it even more efficient and precise.
Key Characteristics of the Elisa Method
When we talk about "elisa del genio," we're really talking about a method with some impressive traits. It's a common laboratory testing technique that finds and counts certain antibodies, antigens, proteins, and hormones in samples. This includes blood, plasma, pee, and saliva. It's pretty versatile, you know, what it can look at.
The method is also very sensitive. This means it can find even tiny amounts of what it's looking for, which is incredibly important for early detection in many situations. It's also a robust method, meaning it gives reliable results time after time. It's actually a very dependable tool for scientists and doctors, which is a big deal.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Detection Target | Antibodies, antigens, proteins, hormones. |
| Sample Types | Blood, plasma, urine, saliva, and other bodily fluids. |
| Sensitivity | Very high, able to detect minute quantities. |
| Specificity | Highly specific, targets particular substances with precision. |
| Quantitation | Can measure the exact amount of a substance present. |
| Applications | Medicine, plant pathology, biotechnology, quality control. |
How Elisa Works: The Core Principles
At its heart, ELISA, like other types of immunoassays, uses the very specific way that antibodies and antigens connect. Think of it like a lock and key. An antibody is like a specific key, and it will only fit with its matching antigen, which is the lock. This very precise pairing is what makes ELISA so powerful. It's a pretty neat trick, honestly.
In the most simple form of an ELISA, this connection is made visible using an enzyme. This enzyme causes a color change when a special substance is added. The intensity of the color tells you how much of the target substance was there. So, a stronger color means more of what you're looking for. It's a really clever way to get a clear answer, you know, just by looking at the color.
Learn about the different methods for performing an ELISA assay for protein quantitation, including assay design strategies and reagents. This involves careful planning to make sure the test works just right. You have to pick the right "keys" and "locks" for your specific purpose, and that takes some thought, too it's almost a puzzle.
The Many Uses of Elisa: Where It Shines
Elisa has been used as a diagnostic tool in medicine, plant pathology, and biotechnology, as well as a quality control check in various industries. Its versatility is truly one of its "genius" aspects. It helps us understand health in many living things, not just people. It's pretty amazing, really, how broadly it can be applied.
In medicine, for example, ELISA tests can detect hormones, bacterial antigens, and antibodies. This means it can help diagnose infections, check hormone levels for certain conditions, or even see if someone has developed immunity to a disease. It's a very important tool for doctors, giving them clear data to work with, you know, when they're trying to figure things out.
Beyond human health, ELISA plays a role in keeping our food safe. It can detect allergens in food products or even diseases in livestock. In plant pathology, it helps identify plant viruses or other issues that could harm crops. So, it's not just about us; it helps protect our food supply and the natural world, which is actually very cool.
Different Types of Elisa Assays
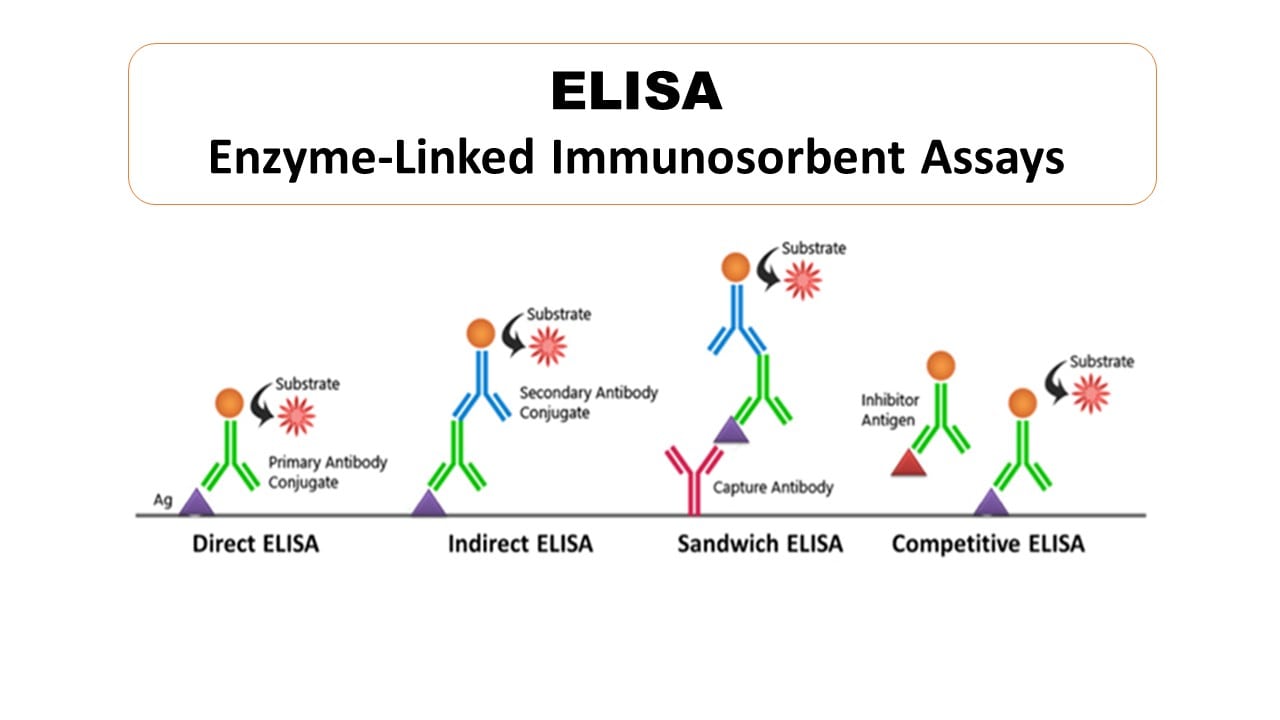
While the basic idea of ELISA stays the same, there are different ways to set up the test, each with its own advantages. Learn about ELISAs (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays) and the various types of ELISA, including direct, indirect, sandwich, and competitive ELISAs. Each type is designed for a slightly different purpose or to give a specific kind of answer. It's sort of like having different tools for different jobs, you know.
Direct ELISA
In a direct ELISA, the antigen is coated directly onto the plate. Then, an enzyme-linked antibody that binds directly to that antigen is added. This is a very straightforward method, often used when you want to quickly detect the presence of a specific antigen. It's pretty simple, actually, which can be good for some uses.
Indirect ELISA
Indirect ELISA uses two antibodies. First, an unlabeled antibody binds to the antigen. Then, a second, enzyme-linked antibody binds to the first antibody. This method is often more sensitive than direct ELISA because it allows for signal amplification. It's a bit more involved, but it can give clearer results, you know, when you need them.
Sandwich ELISA
The sandwich ELISA is considered one of the most sensitive and robust types. Here, a "capture" antibody is coated onto the plate. This antibody grabs the antigen from the sample, like the filling in a sandwich. Then, a second, enzyme-linked "detection" antibody is added, completing the "sandwich." This method is especially good for quantifying antigens in complex samples. It's very precise, too it's almost like building something step by step.
Competitive ELISA
Competitive ELISA is a bit different. In this type, the antigen in the sample "competes" with a known, labeled antigen for binding sites on an antibody. The more antigen there is in your sample, the less labeled antigen will bind, and thus, the weaker the signal will be. This method is often used for very small molecules or when you need to detect low concentrations. It's quite clever, in a way, how it works backwards.
Frequently Asked Questions About Elisa
People often have questions about how ELISA works and what it's for. Here are some common ones that come up, you know, when people are learning about this test.
What is an ELISA test used for?
An ELISA test is used to detect and measure specific substances like antibodies, antigens, proteins, and hormones in various samples. This includes blood, plasma, pee, and saliva. It's used for diagnosing diseases, checking for immunity, and even for quality control in different industries. It's pretty broad in its applications, you know, what it can help with.
How does ELISA detect antigens?
ELISA detects antigens by using specific antibodies that bind to them. An enzyme is attached to one of these antibodies, or to a secondary antibody that binds to the first one. When a special chemical is added, the enzyme reacts with it to produce a color or light signal. The amount of color or light tells you how much antigen was present. It's a very visual way to get an answer, you know, which is helpful.
What are the 4 types of ELISA?
The four main types of ELISA are direct, indirect, sandwich, and competitive. Each type uses a slightly different arrangement of antigens and antibodies to achieve detection. They are chosen based on what is being looked for and the sensitivity needed. It's good to have options, you know, for different situations.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Elisa
The "genius" of ELISA continues to grow. Researchers are always finding ways to make the test even more sensitive, faster, and easier to perform. There are efforts to miniaturize the tests, so they can be done with smaller samples and perhaps even outside of a traditional lab setting. This would make diagnostics more accessible, you know, for more people.
As of today, , ELISA remains a vital tool, especially with new challenges always appearing in public health. Its ability to quickly and accurately identify specific markers makes it incredibly valuable. We can expect to see it adapted and improved even further in the years to come, which is actually very exciting.
This method, Elisa, is a very sensitive immunochemical technique which is used to access the presence of specific protein (antigen or antibody) in the sample. It is a method of quantifying an antigen. It's pretty clear that its role in diagnostics will only become more important. To learn more about how these tests work, you might want to explore resources like the Sigma-Aldrich guide on ELISA, which offers even more technical details.
So, the next time you hear about a diagnostic test, remember the clever principles behind "elisa del genio." It's a method that truly helps us understand the tiny, yet very important, details of our health. Learn more about ELISA technology on our site, and link to this page about our diagnostic methods.
Related Resources:


Detail Author:
- Name : Marie Eichmann V
- Username : doyle.loren
- Email : cummerata.lawrence@gmail.com
- Birthdate : 1994-06-12
- Address : 54478 Kuphal Rest Suite 406 West Lysanneberg, NE 41304-4500
- Phone : 1-972-206-9101
- Company : Stoltenberg Inc
- Job : Business Teacher
- Bio : Deserunt necessitatibus facere laudantium voluptas neque. In earum quia ab. Vero aut numquam at nobis. Enim quia aut aut.
Socials
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/rhea_ernser
- username : rhea_ernser
- bio : Aliquid velit rerum facere ullam unde libero.
- followers : 4121
- following : 1278
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/rhea_official
- username : rhea_official
- bio : Vel placeat eaque commodi quasi vel. Ducimus rerum quo sed sunt aliquam in. Aut repudiandae et neque voluptates.
- followers : 3542
- following : 606
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/rheaernser
- username : rheaernser
- bio : Voluptas dolor omnis iste. Aut rerum porro reiciendis soluta vero. Id explicabo et cumque.
- followers : 4819
- following : 646